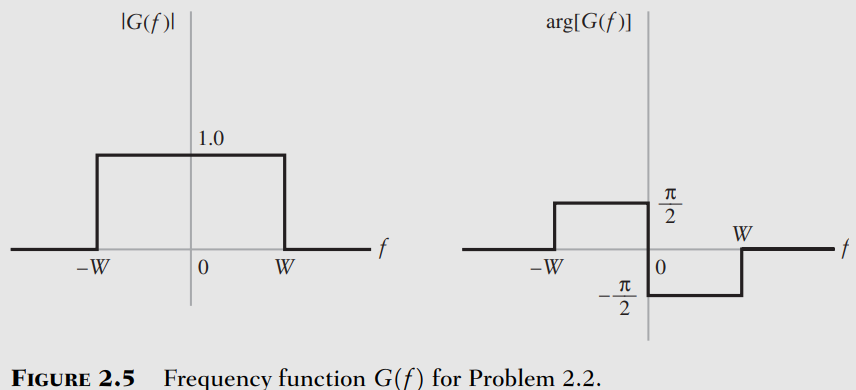
Fourier Transform (Analysis Equation)
The Fourier transform will Uniquely define
For a non-periodic
Inverse Fourier Transform (Synthesis Equation)
Uniquely defines
Fourier Transform is Complex
Dirichlet’s Conditions
If these are satisfied
- Single-valued with finite extrema in any finite interval
- Finite discontinuities in any finite interval
- Absolutely integrable:
All physically realizable functions have a Fourier Transform
Physically realizable functions are all energy functions defined as:
Fourier Transform is Conjugate Symmetric for real time-domain Functions
if
is even
is odd
But if
Inverse Relationship of the Fourier Transform
A pulse narrow in time has a wide range of frequencies and a function defined over a lot of time has a narrow frequency range
Common Fourier Pairs
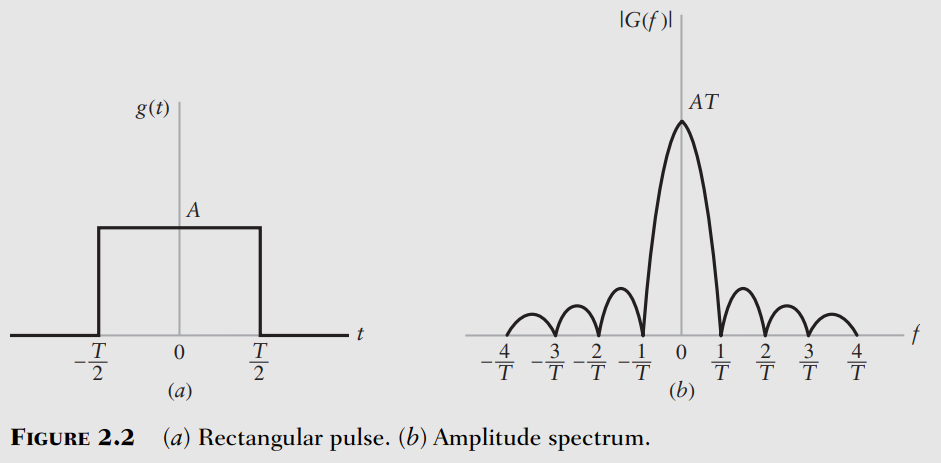
Rectangular Function and Sinc
Rectangular Function
More generally:
Sinc Function
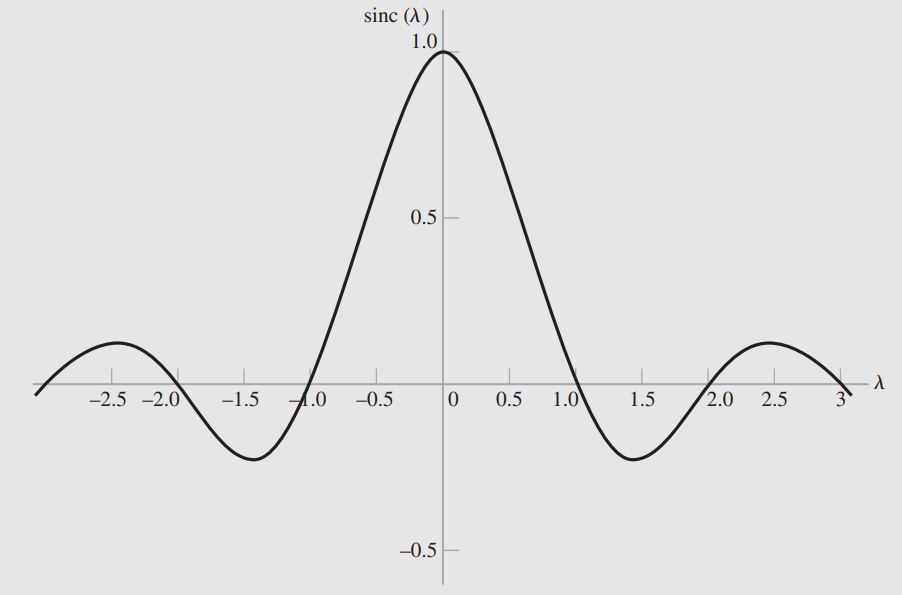
So:
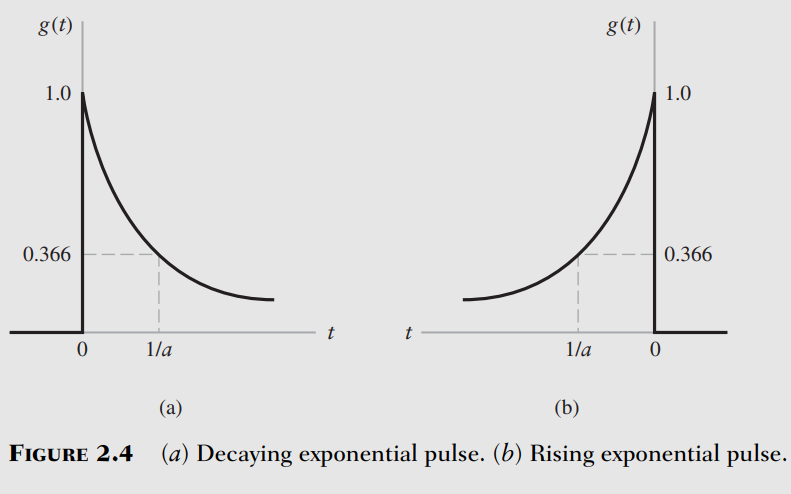
Truncated Decaying Exponential Pulse
Unit Step Function
Decaying Exponential Pulse
Rising Exponential Pulse
Fourier Transform
So: