Amplitude-modulated Wave
is the message or information-bearing signal is the carrier wave is the envelope, this resembles , provided that: , so that is always positive where is the bandwidth of . - This is necessary for detection later on.
is also the highest frequency in , where highest means largest significant frequency rather than the frequency with the highest amplitude. This is because is assumed to be low-pass.
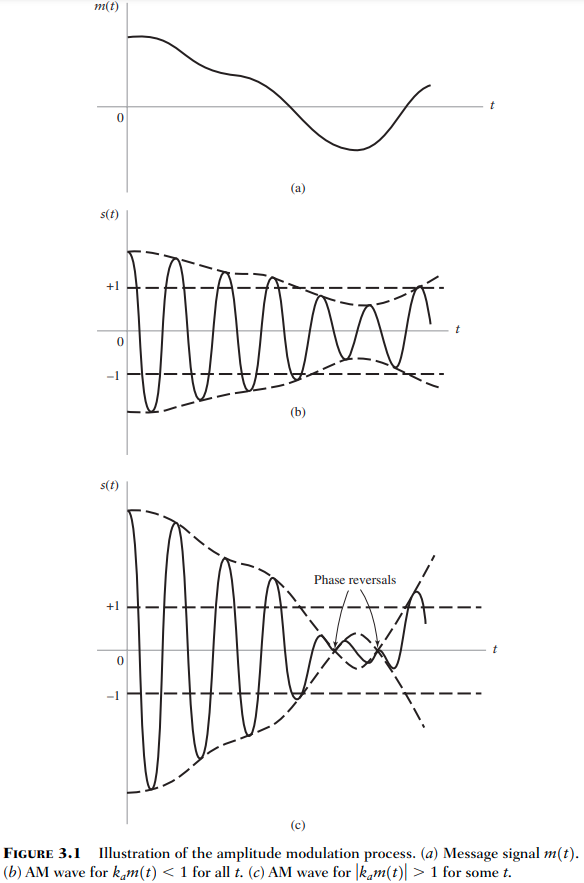
Last one is an example of what we don’t want.
Fourier Transform
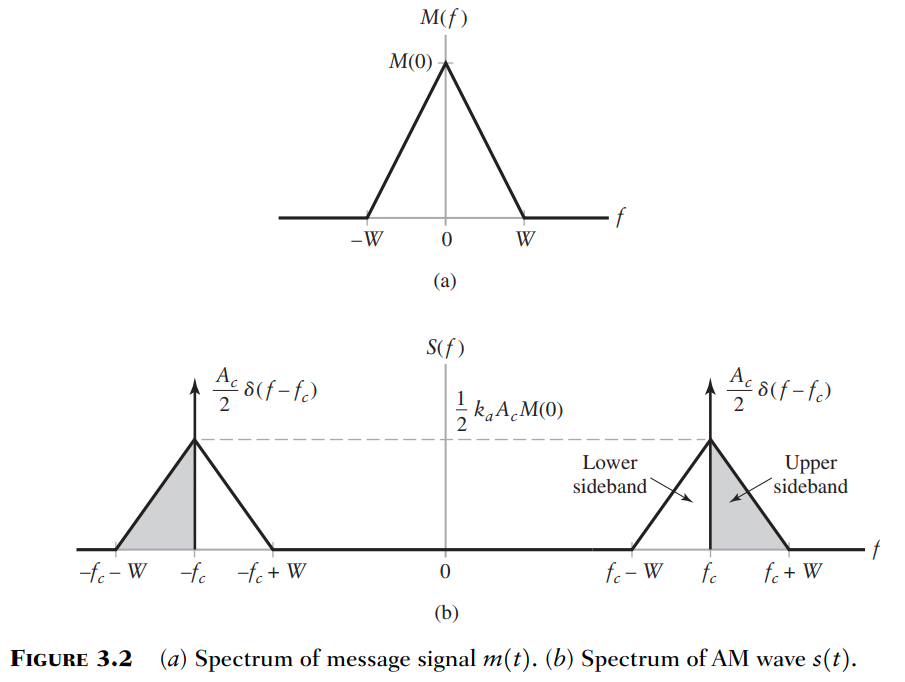
Envelope Detection
The detector works if our the two earlier conditions are satisfied.
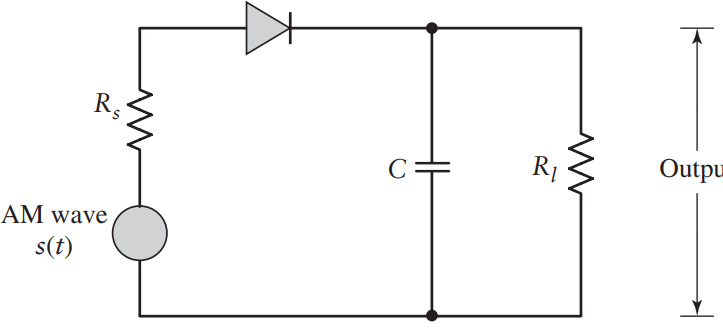
is the internal impedance Operation - Charges quickly when
(forward biased diode) to follow the AM wave - So we want the charging time to be short compared to the carrier period
so the capacitor voltage won’t lag behind
- So we want the charging time to be short compared to the carrier period
- Discharges slowly when
(reverse biased/cutoff) to keep the voltage high - So we want the discharging time to be longer than the carrier period, but fast enough that it discharges faster than the maximum rate of change of the message
- Max rate of change → highest frequency (
)
- The result is that
, the voltage in the capacitor, matches the envelope